[1001] B Cell Humoral Immune Response Free
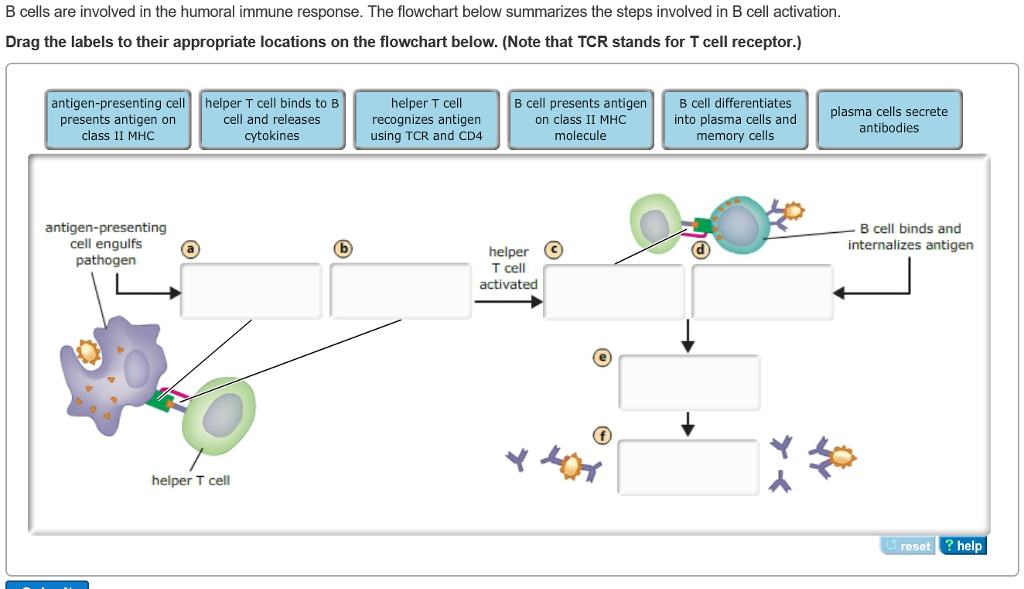
B cell activation b cells must be activated by an antigen before they can fight pathogens.
[78] B Cell Humoral Immune Response Free. Each b cell has a unique antibody that binds with an antigen. The response follows this chain of events. One direct consequence of the loss of b cell activity on the individual s humoral immune response to an initial exposure to a bacterial pathogen.
Compare the primary and secondary antibody responses humoral immunity refers to mechanisms of the adaptive immune defenses that are mediated by antibodies secreted by b lymphocytes or b cells. This section will focus on b cells and discuss their production and maturation receptors and mechanisms of activation. B acquired humoral immunity.
Antigens bind to b cells. These membrane bound protein complexes have antibodies which are specific for antigen detection. The humoral immune response involves mainly b cells and takes place in blood and lymph.
The humoral response or antibody mediated response involves b cells that recognize antigens or pathogens that are circulating in the lymph or blood humor is a medieval term for body fluid. These in turn stimulate the complex pathways of the cell mediated immune response and the humoral immune response respectively. Humoral immunity is an aspect of specific immune responses directed at particular antigens.
Interleukins or helper t cells costimulate b cells. The mature b cells migrate from the bone marrow to the lymph nodes or other lymphatic organs where they begin to encounter pathogens. Functional analyses reveal that til b are responsive to b cell receptor bcr stimulation ex vivo express activation markers and produce cytokines and igs despite reduced expression of the antigen presenting molecules hla dr and cd40.
Stimulation of immune response by activated helper t cells. Daruna in introduction to psychoneuroimmunology second edition 2012. Activated by complex interaction with molecules on the surface of a macrophage or some other antigen presenting cell a helper t cell proliferates into two general subtypes t h 1 and t h 2.
Emerging evidence suggest a role for b cell and humoral immunity in the control of intracellular pathogens including obligatory species through interactions with the cell mediated immune compartment. With assistance from helper t cells b cells will differentiate into plasma b cells that can produce antibodies against a specific. It takes the form of unique antibodies produced by b lymphocytes that have been specifically selected to neutralize the antigen at hand.
Proposal 1 point does not produce antibodies does not produce memory b cells. Humoral immunity is also called antibody mediated immunity.
































.PNG)




.jpg)























































